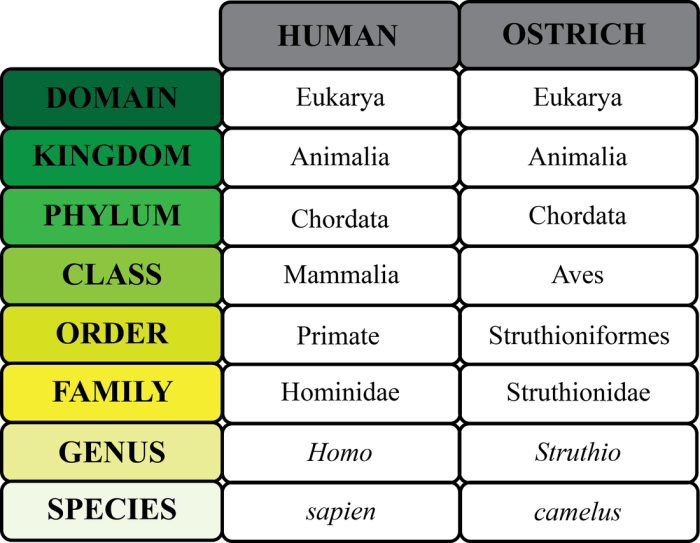
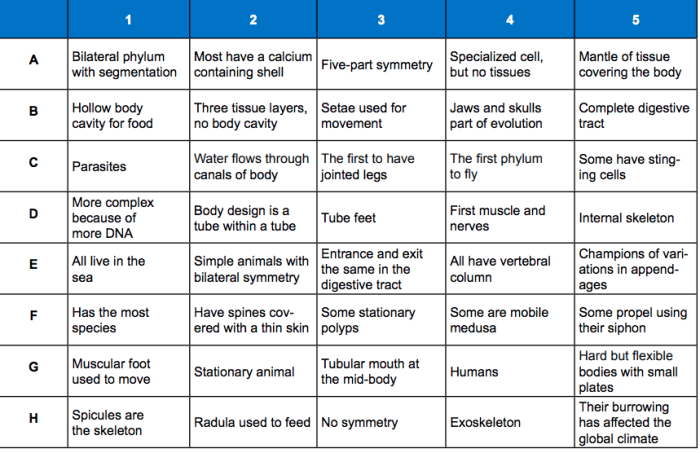
Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key is an invaluable tool for scientists and researchers seeking to identify and classify organisms. This comprehensive key provides a systematic approach to identifying organisms based on their physical characteristics, making it an essential resource for taxonomists and biologists alike.
The key is organized into a hierarchical structure, with each level representing a different taxonomic rank. Starting with the phylum level, the key guides users through a series of dichotomous choices, each of which leads to a more specific classification.
This user-friendly format makes it easy to navigate and identify organisms even for those with limited taxonomic experience.
Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key
Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key is a tool used to identify organisms based on their physical characteristics. It is organized into a series of steps, each of which presents a set of characteristics that can be used to distinguish between different groups of organisms.
The table 2 phylum taxonomic key is a handy tool for identifying organisms. If you’re wondering what day it is today, simply click qué fecha es el día de hoy . After checking the date, you can continue using the table 2 phylum taxonomic key to classify organisms.
To use the key, start at the first step and read the characteristics listed. If the organism you are trying to identify matches the characteristics in a particular step, move on to the next step. If the organism does not match the characteristics in a particular step, move on to the next step that is indicated in the key.
Using the Key
As you move through the key, you will be presented with a series of choices. Each choice will lead you to a different part of the key. The choices will become more specific as you move through the key, and eventually you will reach a point where you can identify the organism to the phylum level.
It is important to note that the key is not always 100% accurate. There are some organisms that may not fit perfectly into the key. However, the key can be a valuable tool for identifying organisms, and it can help you to learn more about the diversity of life on Earth.
Key Features
Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key is a valuable tool for identifying organisms based on their specific characteristics. The key provides a series of questions and answers that guide users through the identification process, leading to the correct phylum.
The key features of Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key include:
- Clear and concise questions:The questions in the key are straightforward and easy to understand, allowing users to quickly determine which characteristics to examine in the organism.
- Dichotomous format:The key follows a dichotomous format, where each question leads to two possible answers. This structure allows users to efficiently narrow down the options and identify the correct phylum.
- Relevant and informative answers:The answers to the questions provide valuable information about the characteristics of different phyla. This information helps users understand the basis for the identification and distinguish between similar organisms.
- Comprehensive coverage:The key covers a wide range of phyla, ensuring that users can identify most common organisms encountered in various environments.
Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key depend on the accuracy of the information it contains. The key is based on well-established taxonomic principles and has been carefully compiled by experts in the field. However, it is important to note that the key may not be able to identify all organisms, especially those that are newly discovered or have unusual characteristics.
Phylum Classification
The phyla listed in Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key represent a diverse array of organisms, each exhibiting unique characteristics that distinguish them from other groups. These phyla are classified based on a combination of morphological, biochemical, and genetic criteria.
Morphological characteristics, such as body structure, symmetry, and appendages, provide valuable insights into the evolutionary relationships between different organisms. Biochemical analyses, including comparisons of DNA and RNA sequences, help identify shared genetic traits and determine the relatedness of different species.
Additionally, the presence or absence of specific molecules, such as chlorophyll or cell walls, further contributes to the classification of organisms into different phyla.
Phyla Included in Table 2
- Porifera (sponges)
- Cnidaria (jellyfish, corals, sea anemones)
- Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
- Nematoda (roundworms)
- Annelida (segmented worms)
- Mollusca (clams, snails, octopuses)
- Arthropoda (insects, spiders, crustaceans)
- Echinodermata (starfish, sea urchins, sea cucumbers)
- Chordata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals)
Practical Applications
Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key finds practical applications in various fields, aiding in the identification and classification of organisms. It serves as a valuable tool for researchers, taxonomists, and ecologists.
Field Research
- Identification of organisms in the field, particularly when access to sophisticated equipment or expertise is limited.
- Rapid assessment of biodiversity, allowing researchers to gain insights into the composition and diversity of ecosystems.
Laboratory Research
- Verification of species identification in laboratory studies, ensuring accurate and reliable data.
- Molecular studies, where the key provides a framework for understanding the evolutionary relationships among different phyla.
Education
- Teaching tool for students learning about taxonomy and the diversity of life.
- Citizen science initiatives, engaging the public in biodiversity monitoring and data collection.
Conservation and Management
- Identification of threatened or endangered species, aiding in conservation efforts and habitat protection.
- Assessment of the impact of human activities on ecosystems, such as pollution or habitat destruction.
Limitations and Considerations: Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key
While Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key is a valuable tool for identifying phyla, it is essential to recognize its limitations and factors that can influence the accuracy of identification.
Accuracy Factors
The accuracy of identification using Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key depends on several factors, including:
- Specimen quality:Poorly preserved or incomplete specimens may not exhibit all the necessary characteristics for accurate identification.
- Observer expertise:Identification requires trained observers who can correctly interpret the key’s characteristics.
- Morphological variations:Some species within a phylum may exhibit variations in their morphological features, potentially complicating identification.
Limitations
Despite its usefulness, Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key has certain limitations:
- Limited scope:The key is only applicable to identifying phyla and does not provide further classification to lower taxonomic levels.
- Potential for misidentification:Incorrect interpretation of key characteristics or the presence of atypical specimens can lead to misidentification.
- Lack of molecular data:The key relies solely on morphological characteristics and does not incorporate molecular data, which can provide additional insights into species relationships.
Advanced Techniques
Advanced techniques, such as molecular analysis and microscopy, can be used in conjunction with Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key to enhance the identification process. Molecular analysis, such as DNA sequencing, can provide genetic information that can be used to identify organisms to the species level.
Microscopy, such as electron microscopy, can provide detailed images of an organism’s structure, which can be used to identify it to the genus or species level.
Molecular Analysis, Table 2 phylum taxonomic key
Molecular analysis involves the study of an organism’s DNA or RNA. This can be done by extracting the genetic material from the organism and sequencing it. The sequence of the genetic material can then be compared to a database of known sequences to identify the organism.
Molecular analysis is a powerful tool for identifying organisms, as it can be used to identify organisms that are difficult to identify using traditional methods. For example, molecular analysis can be used to identify bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics.
Microscopy
Microscopy is the study of organisms using a microscope. Microscopes can be used to magnify an organism’s structure, which can help to identify it. Electron microscopy is a type of microscopy that uses a beam of electrons to create a detailed image of an organism’s structure.
Electron microscopy can be used to identify organisms to the genus or species level. For example, electron microscopy can be used to identify the different types of bacteria that cause pneumonia.
Future Developments
The field of taxonomic keys is constantly evolving, with new developments emerging regularly. These developments have the potential to significantly impact the use of Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key.
One of the most promising developments is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to automate the process of key construction. AI algorithms can be trained on large datasets of taxonomic data, and then used to generate keys that are both accurate and efficient.
Potential Impact on Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key
The use of AI to automate key construction could have a number of benefits for Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key. First, it could make the key more accurate and reliable. Second, it could make the key easier to use, especially for non-experts.
Third, it could make the key more efficient to use, saving time and resources.
Clarifying Questions
What is the purpose of Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key?
Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key is designed to assist in the identification and classification of organisms based on their physical characteristics.
How do I use Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key?
The key is organized into a hierarchical structure. Start at the phylum level and follow the dichotomous choices to narrow down the classification.
What are the limitations of Table 2 Phylum Taxonomic Key?
The key may not be able to identify all organisms, especially those with unusual or intermediate characteristics.