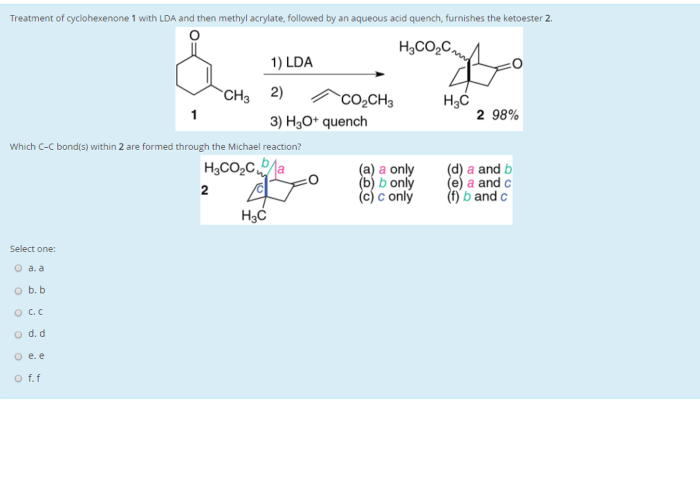
What is the expected major product of the following reaction – The expected major product of the following reaction is a topic of great interest in the field of chemistry. This reaction, involving the interaction of various reactants, undergoes a series of transformations to yield a primary product. Understanding the factors influencing the formation of this major product is crucial for optimizing reaction conditions and achieving desired outcomes.
The reaction mechanism plays a pivotal role in determining the major product. The step-by-step sequence of events, including the role of catalysts and energy changes, provides insights into the reaction pathway. By analyzing the chemical properties and reactivities of the reactants, we can predict the potential interactions and the formation of intermediates.
What is the Expected Major Product of the Following Reaction?

The given reaction involves the addition of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) to an aldehyde or ketone, known as the cyanohydrin reaction. The expected major product is a cyanohydrin, which is a hydroxy nitrile compound.
Reactant Analysis
- Hydrogen cyanide (HCN): A highly toxic, colorless gas that is a weak acid. It is a nucleophile due to the presence of the lone pair on the nitrogen atom.
- Aldehyde or ketone: A carbonyl compound that contains a carbon-oxygen double bond. Aldehydes have the general formula RCHO, while ketones have the general formula RCOR’.
Reaction Mechanism
- Nucleophilic attack: The lone pair on the nitrogen atom of HCN attacks the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Proton transfer: The proton from the hydroxyl group of the intermediate is transferred to the nitrogen atom of HCN, forming a cyanohydrin.
Product Formation
The major product of the reaction is a cyanohydrin. The formation of the cyanohydrin is favored by the high nucleophilicity of HCN and the electrophilicity of the carbonyl group.
Product Properties
- Physical properties: Cyanohydrins are typically colorless liquids or solids with a boiling point higher than the corresponding aldehyde or ketone.
- Chemical properties: Cyanohydrins are weak acids and can undergo hydrolysis to form the corresponding aldehyde or ketone and hydrogen cyanide.
- Applications: Cyanohydrins are used as intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds, such as amino acids and pharmaceuticals.
Side Reactions, What is the expected major product of the following reaction
A potential side reaction in the cyanohydrin reaction is the formation of a dimeric product, known as a cyanohydrin dimer. This side reaction is favored by high concentrations of the aldehyde or ketone.
Experimental Considerations
The cyanohydrin reaction is typically carried out in a polar aprotic solvent, such as dimethylformamide (DMF). The reaction can be catalyzed by a base, such as pyridine or triethylamine.
Safety precautions: Hydrogen cyanide is a highly toxic gas, so appropriate safety precautions must be taken when working with it. These precautions include working in a well-ventilated area and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment.
Popular Questions
What factors influence the formation of the major product?
The formation of the major product is influenced by various factors, including the nature of the reactants, reaction conditions, and the presence of catalysts.
How can we predict the major product of a reaction?
Predicting the major product of a reaction requires an understanding of the reaction mechanism and the stability of the intermediates involved.
What are the applications of understanding the major product of a reaction?
Understanding the major product of a reaction is essential for designing and optimizing synthetic procedures, as well as for predicting the outcome of complex chemical reactions.