How did Boyle’s research transform chemistry into a real science? Robert Boyle’s groundbreaking contributions to chemistry in the 17th century revolutionized the field, establishing it as a true science based on experimentation and quantitative data. His pioneering work laid the foundation for modern chemistry, shaping our understanding of the behavior of gases, the nature of matter, and the development of a standardized chemical nomenclature.
Boyle’s emphasis on experimentation and the collection of quantitative data transformed chemistry from a qualitative to a quantitative science. He challenged the prevailing Aristotelian view of matter, proposing a corpuscular theory that laid the groundwork for modern atomic theory. Boyle’s experiments led to the formulation of the Boyle-Mariotte Law, a fundamental principle that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of gases.
Boyle’s Contributions to the Scientific Method: How Did Boyle’s Research Transform Chemistry Into A Real Science

Boyle merevolusi kimia dengan menekankan eksperimentasi dan data kuantitatif. Eksperimennya yang cermat dan terdokumentasi dengan baik menggantikan pendekatan kualitatif yang dominan, yang mengandalkan pengamatan dan deskripsi subjektif.
Boyle menetapkan metodologi ilmiah sebagai dasar kimia. Dia menekankan pentingnya kontrol variabel, pengulangan eksperimen, dan pengukuran yang akurat. Pendekatan sistematis ini memungkinkan para ilmuwan untuk menguji hipotesis secara objektif dan menarik kesimpulan yang didukung oleh bukti.
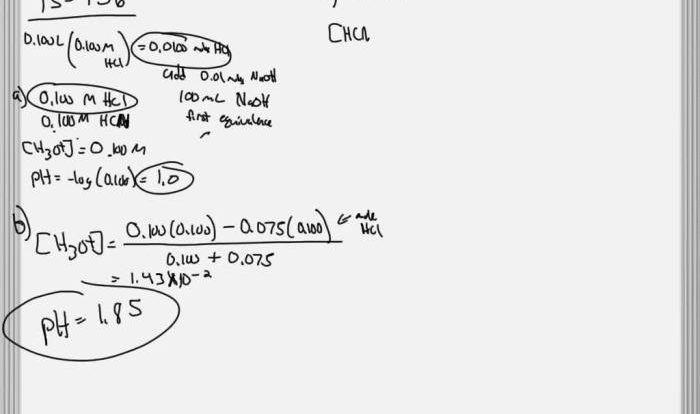
The Boyle-Mariotte Law
Boyle-Mariotte Law adalah persamaan matematika yang menggambarkan hubungan antara tekanan dan volume gas pada suhu konstan. Hukum ini menyatakan bahwa pada suhu konstan, tekanan gas berbanding terbalik dengan volumenya.
Eksperimen Boyle mengarah pada perumusan hukum ini. Dia mengompresi udara dalam tabung tertutup dan mengamati bahwa ketika volume udara berkurang, tekanannya meningkat. Hasil ini mengkonfirmasi hubungan terbalik antara tekanan dan volume.
Boyle-Mariotte Law memiliki aplikasi luas dalam berbagai bidang, termasuk fisika, teknik, dan kimia. Ini digunakan untuk merancang mesin, memahami sifat gas, dan memprediksi perilaku sistem gas.
The Corpuscular Theory of Matter

Teori korpuskular Boyle menantang pandangan Aristoteles yang menyatakan bahwa materi adalah kontinum yang dapat dibagi tanpa batas. Boyle berpendapat bahwa materi terdiri dari partikel-partikel kecil dan tidak terpisahkan yang disebut korpuskula.
Teori Boyle memiliki beberapa prinsip utama:
- Materi terdiri dari partikel-partikel kecil dan tidak dapat dibagi yang disebut korpuskula.
- Korpuskula bergerak dan bertabrakan satu sama lain.
- Sifat-sifat materi ditentukan oleh ukuran, bentuk, dan gerakan korpuskula.
Teori Boyle meletakkan dasar bagi teori atom modern dan berkontribusi pada pemahaman kita tentang struktur materi.
Boyle’s Influence on Chemical Nomenclature
Boyle memainkan peran penting dalam pengembangan nomenklatur kimia yang terstandarisasi. Dia mengusulkan sistem penamaan yang didasarkan pada sifat kimia suatu zat.
Sistem Boyle membantu menciptakan bahasa yang sama bagi para ahli kimia, memungkinkan mereka untuk berkomunikasi dan bertukar informasi dengan jelas. Ini memfasilitasi kolaborasi ilmiah dan pemahaman yang lebih baik tentang sifat-sifat dan reaksi zat kimia.
Sistem nomenklatur Boyle masih menjadi dasar sistem yang digunakan dalam kimia modern, yang memastikan konsistensi dan akurasi dalam mengidentifikasi dan mendeskripsikan senyawa kimia.
Questions Often Asked
What was Boyle’s most significant contribution to chemistry?
Boyle’s most significant contribution to chemistry was his emphasis on experimentation and quantitative data, which transformed chemistry from a qualitative to a quantitative science.
How did Boyle’s research contribute to the development of the scientific method?
Boyle played a crucial role in establishing the scientific method as the foundation of chemistry. He emphasized the importance of experimentation, observation, and the collection of quantitative data to support scientific theories.
What is the Boyle-Mariotte Law and what is its significance?
The Boyle-Mariotte Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of gases at constant temperature. It is a fundamental principle that has applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
How did Boyle’s corpuscular theory of matter challenge the prevailing Aristotelian view?
Boyle’s corpuscular theory of matter challenged the Aristotelian view that matter was continuous and infinitely divisible. Boyle proposed that matter was composed of tiny, indivisible particles, which laid the foundation for modern atomic theory.
What was Boyle’s contribution to the development of chemical nomenclature?
Boyle played a significant role in the development of a standardized chemical nomenclature. He introduced a system of naming chemical compounds based on their composition and properties, which helped establish a common language for chemists.