Which of the following statement about oligopolies is true? Oligopolies, characterized by a small number of dominant firms controlling a significant market share, present unique dynamics that shape industry behavior and economic outcomes. This article delves into the intricacies of oligopolistic market structures, pricing strategies, entry barriers, and the implications for market power and economic efficiency.
Understanding the nuances of oligopolies is crucial for policymakers, industry analysts, and business leaders seeking to navigate the complexities of these concentrated markets.
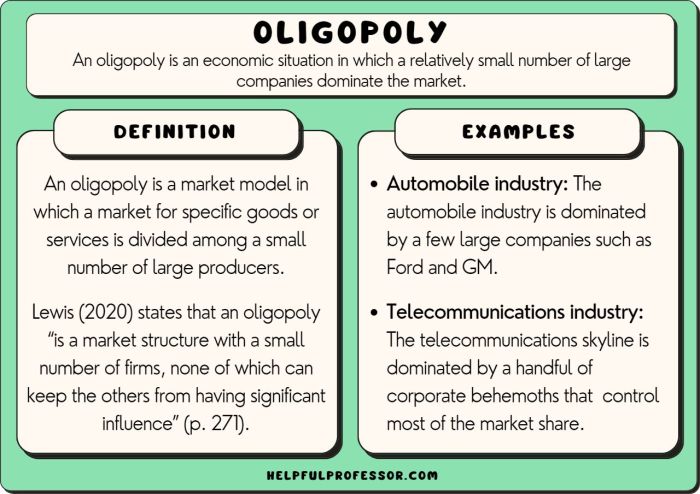
Market Structure of Oligopolies
An oligopoly is a market structure characterized by the presence of a few large firms that dominate the industry. These firms have significant market power, as they control a large share of the market and can influence prices and output.
Examples of industries that exhibit oligopolistic behavior include the automobile industry, the telecommunications industry, and the pharmaceutical industry.
Factors Contributing to the Formation of Oligopolies
- High barriers to entry: Oligopolies often exist in industries where there are significant barriers to entry, such as high capital costs, economies of scale, or patents.
- Product differentiation: Oligopolies can also form when firms differentiate their products, creating brand loyalty and making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share.
- Government regulations: Government regulations can also contribute to the formation of oligopolies by limiting the number of firms that can operate in a particular industry.
Pricing Behavior in Oligopolies

Oligopolies face unique challenges when it comes to pricing. Due to their market power, oligopolies can set prices above marginal cost, but they must also consider the reactions of their rivals. As a result, oligopolies often engage in different pricing strategies.
Price Leadership, Which of the following statement about oligopolies is true
Price leadership is a pricing strategy in which one firm in the industry sets the price, and other firms follow suit. This can occur when one firm has a dominant market share or a reputation for being a price leader.
Collusion and Cartels
Collusion is an agreement between firms to set prices or output levels. Cartels are formal agreements that are designed to eliminate competition and maximize profits. Collusion and cartels are illegal in many countries, but they can still occur in practice.
Entry Barriers and Competition: Which Of The Following Statement About Oligopolies Is True
Oligopolies often have high barriers to entry, which can limit competition and reduce market efficiency. These barriers can include:
Economies of Scale
Economies of scale occur when firms can produce more output at a lower cost per unit. This can create a barrier to entry for new firms, as they may not be able to achieve the same level of efficiency as the incumbent firms.
Product Differentiation
Product differentiation can also create a barrier to entry by making it difficult for new firms to gain market share. Consumers may be loyal to a particular brand or product, making it difficult for new firms to enter the market.
Government Regulations
Government regulations can also create barriers to entry by limiting the number of firms that can operate in a particular industry. This can occur through licensing requirements, zoning restrictions, or other regulations.
Market Power and Economic Efficiency
Oligopolies possess significant market power, which can lead to inefficiencies in the market. These inefficiencies can include:
Higher Prices
Oligopolies can set prices above marginal cost, which can lead to higher prices for consumers.
Reduced Output
Oligopolies may also reduce output in order to maximize profits, which can lead to shortages and higher prices.
Lack of Innovation
Oligopolies may also have less incentive to innovate, as they may be able to maintain their market share without investing in new products or processes.
Questions and Answers
What is the primary characteristic of an oligopoly market structure?
A small number of dominant firms control a majority of the market share.
How do oligopolies influence pricing decisions?
Oligopolies often engage in strategic pricing behaviors, such as price leadership and collusion, to maintain market power.
What factors contribute to the formation of oligopolies?
Economies of scale, high entry barriers, and product differentiation are common factors that lead to the formation of oligopolies.