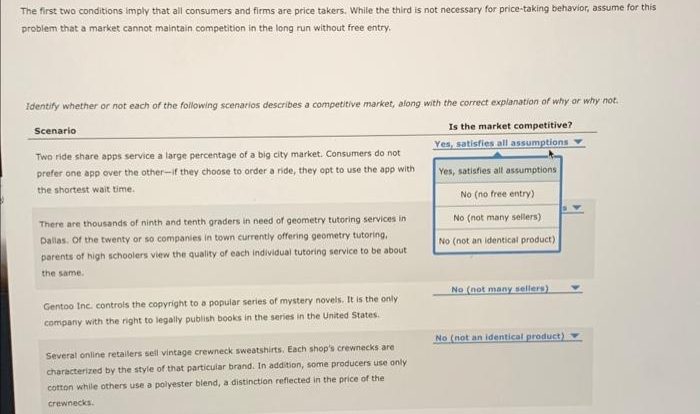
For each person to an economist crossword clue – The concept of “for each person to an economist” is a fundamental principle in economic theory, capturing the idea that each individual’s unique preferences and consumption patterns shape the overall functioning of the economy. This concept serves as the foundation for understanding consumer behavior, market equilibrium, and government intervention in economic systems.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of this concept, exploring its implications for economic decision-making, market dynamics, and policy formulation. Through a rigorous examination of economic principles and real-world examples, we unravel the complexities of how individual choices collectively influence economic outcomes.
Economic Concepts

Economic concepts provide the foundation for understanding how economies operate. These concepts include:
Marginal Utility
Marginal utility is the additional satisfaction a consumer derives from consuming one more unit of a good or service. As consumers consume more of a good, the marginal utility they derive from each additional unit decreases, a phenomenon known as diminishing marginal utility.
Diminishing Marginal Utility
Diminishing marginal utility affects consumption decisions by influencing the point at which consumers choose to stop consuming a good or service. Consumers will continue to consume until the marginal utility of the next unit is equal to the marginal cost of acquiring it.
Individual Preferences
Marginal utility helps explain individual preferences. Consumers prefer goods and services that provide them with the greatest marginal utility, taking into account both the satisfaction they derive from the good and the cost of acquiring it.
Consumer Behavior: For Each Person To An Economist Crossword Clue
Consumer behavior is the study of how individuals make decisions about consuming goods and services. Factors that influence consumer demand include:
Income
Income is a primary determinant of consumer demand. As income increases, consumers can afford to purchase more goods and services.
Prices
Prices influence consumer demand through the law of demand, which states that as prices increase, demand for a good or service decreases.
Preferences
Preferences are subjective factors that influence consumer demand, such as personal tastes, beliefs, and cultural norms.
Market Equilibrium
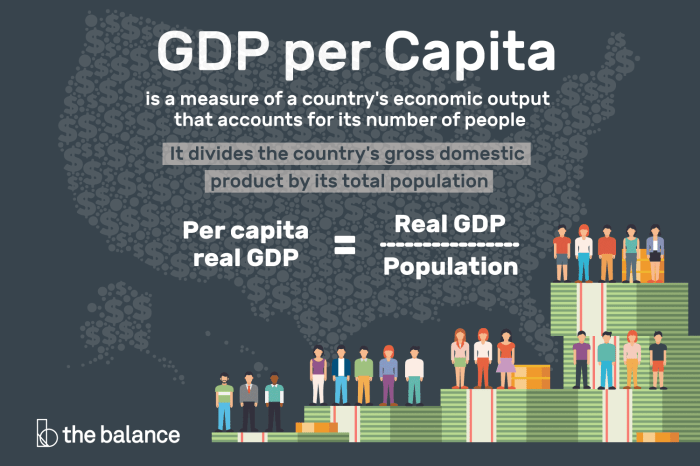
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied equals the quantity demanded. The equilibrium price is the price at which this occurs.
Role of Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are the two primary forces that determine equilibrium prices. Supply is the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to sell, while demand is the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy.
Market Equilibrium in Different Industries, For each person to an economist crossword clue
Market equilibrium can be observed in various industries, such as the housing market, the labor market, and the stock market.
Government Intervention
Government intervention refers to policies and actions taken by governments to influence economic outcomes. Common types of government intervention include:
Price Controls
Price controls are government-imposed limits on the prices of goods and services.
Subsidies
Subsidies are government payments to producers or consumers to encourage certain economic activities.
Taxes
Taxes are government-imposed levies on individuals or businesses to generate revenue or influence economic behavior.
Economic Measurement

Economic measurement is essential for assessing economic performance and making informed decisions. Key economic indicators include:
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period.
Inflation
Inflation measures the rate of increase in the general price level of goods and services.
Unemployment Rates
Unemployment rates measure the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
International Economics
International economics focuses on economic relationships between countries. Key concepts include:
Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage refers to the ability of countries to produce goods and services more efficiently than other countries.
Free Trade
Free trade refers to the absence of government restrictions on the import and export of goods and services.
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasing interconnectedness of the world’s economies through trade, investment, and technology.
Top FAQs
What is the significance of individual preferences in economic theory?
Individual preferences play a central role in economic theory, as they determine the demand for goods and services in the market. Understanding consumer preferences is crucial for businesses to develop products and services that meet market needs and for policymakers to design policies that align with the well-being of citizens.
How does diminishing marginal utility affect consumption decisions?
Diminishing marginal utility suggests that as individuals consume more of a particular good or service, the additional satisfaction or utility they derive from each additional unit decreases. This principle influences consumption decisions by leading individuals to allocate their resources efficiently, seeking a balance between the satisfaction gained from consuming different goods and services.
What is the role of government intervention in the economy?
Government intervention in the economy can take various forms, including price controls, subsidies, and taxes. Governments intervene to correct market failures, promote economic growth, and ensure the well-being of citizens. However, government intervention can also lead to unintended consequences and inefficiencies, making it a complex and often debated topic.