In this exploration of the capitalism and communism venn diagram, we delve into the fundamental economic structures, political ideologies, and social implications that shape these contrasting systems. From their historical origins to their impact on contemporary societies, we uncover the complexities and overlaps that define capitalism and communism.
The journey begins with an examination of the core economic principles that govern each system, including private property rights, market competition, and government intervention. We then explore the political ideologies that underpin these economic structures, analyzing the role of the state, individual rights, and social equality.
Economic Structures
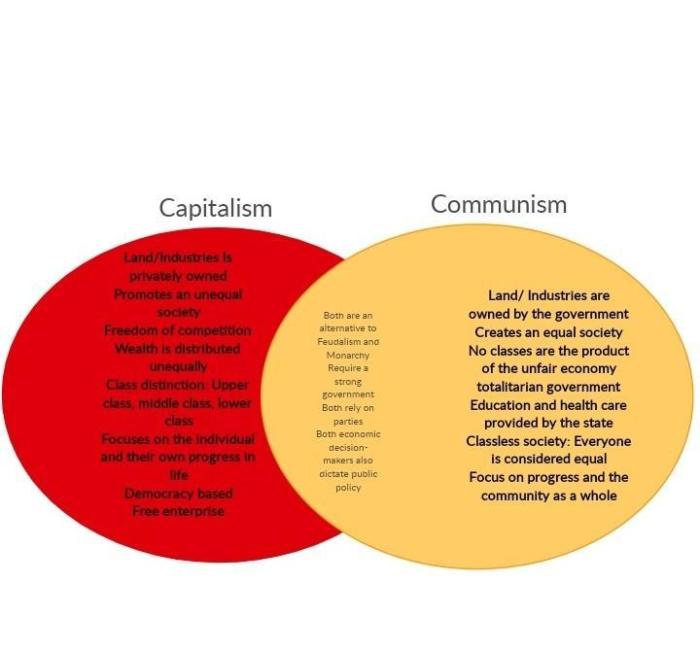
Capitalism and communism are two distinct economic systems that have shaped the world’s economies. Capitalism is characterized by private ownership of capital and the means of production, while communism is characterized by collective or state ownership of the means of production.
Capitalism
Capitalism is based on the principles of private property, free markets, and profit maximization. In a capitalist system, individuals and businesses own and control the means of production, such as factories, land, and equipment. They use these resources to produce goods and services, which they then sell in the market for profit.
- Private ownership of capital and the means of production
- Free markets and competition
- Profit maximization
- Limited government intervention in the economy
Examples of countries that have adopted capitalist systems include the United States, the United Kingdom, and Japan.
Communism
Communism is an economic system in which the means of production are collectively owned and controlled by the state or a cooperative. In a communist system, the government plans and directs the economy, and individuals receive goods and services based on their needs, rather than their ability to pay.
- Collective ownership of the means of production
- Central planning and government control of the economy
- Distribution of goods and services based on need
- Limited private property
Examples of countries that have adopted communist systems include China, Cuba, and the former Soviet Union.
Political Ideologies
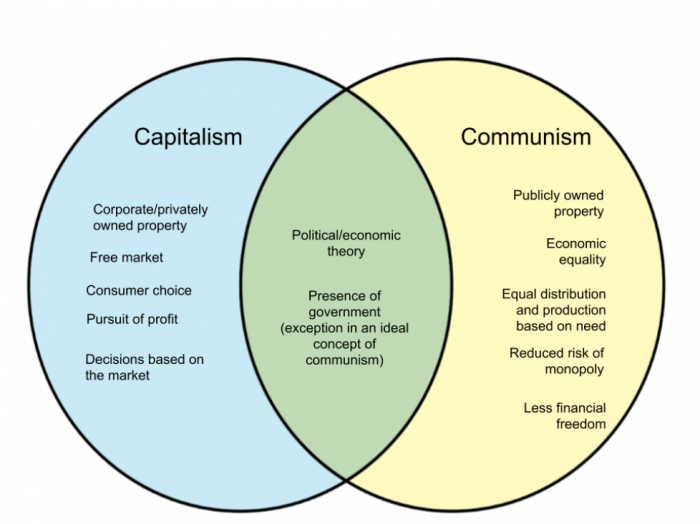
Capitalism and communism represent contrasting political ideologies that shape their respective economic systems. Capitalism is rooted in private ownership of property and free markets, while communism advocates for collective ownership and central planning.
The political ideologies underlying these systems significantly influence their approaches to government, individual rights, and freedoms.
Role of Government
In capitalist societies, the role of government is generally limited to maintaining law and order, enforcing contracts, and providing essential public services like infrastructure and education. The private sector plays a dominant role in the economy, with minimal government intervention.
In contrast, communist governments exercise extensive control over the economy, including the allocation of resources, production, and distribution. The state owns and manages key industries, and government officials make decisions regarding economic planning and development.
Individual Rights and Freedoms
Capitalism places a high value on individual rights and freedoms, including the right to private property, freedom of speech, and freedom of assembly. Economic freedom is also emphasized, with individuals free to pursue their own economic interests.
In communist systems, individual rights and freedoms are often subordinated to the collective good. The state may restrict individual freedoms to promote social equality and economic development. Freedom of speech, assembly, and religion may be limited to ensure political stability and prevent dissent.
Social Structures

Under capitalism and communism, distinct social structures emerge, shaped by the distribution of wealth, income, and the role of social class and mobility.
Distribution of Wealth and Income
- Capitalism:Private ownership of capital and means of production leads to unequal distribution of wealth and income. The wealthy elite controls a significant share, while the majority experiences economic disparities.
- Communism:Theoretically, wealth and income are distributed equally among citizens. However, in practice, inequalities may arise due to factors such as political power or bureaucratic privileges.
Social Class and Mobility
- Capitalism:Social classes are defined by economic status and access to resources. Social mobility is possible through individual effort and achievement, but economic barriers can hinder upward mobility for the disadvantaged.
- Communism:Class distinctions are officially abolished, with the goal of creating a classless society. However, social hierarchies and inequalities may still exist based on factors such as education, occupation, or political connections.
Historical Context
Capitalism and communism emerged as distinct economic and political ideologies during the 19th century, reflecting the profound social and economic transformations of the Industrial Revolution.
Major Events and Thinkers
- French Revolution (1789-1799):A watershed moment that challenged the traditional feudal order and laid the groundwork for the rise of capitalism.
- Industrial Revolution (late 18th-19th centuries):The advent of industrial production and technological advancements created new economic and social structures, fostering the growth of capitalism.
- Karl Marx (1818-1883):A German philosopher and economist who developed the theory of communism, arguing that capitalism was inherently exploitative and would inevitably be overthrown by a workers’ revolution.
- Vladimir Lenin (1870-1924):A Russian revolutionary leader who implemented the first communist state in the Soviet Union.
Impact on World History
- Economic Growth:Capitalism has driven unprecedented economic growth and technological advancements, leading to increased productivity and living standards for many.
- Social Inequality:Capitalism’s emphasis on individual profit has also resulted in significant social inequality, with wealth concentrated in the hands of a few.
- Political Conflicts:The ideological divide between capitalism and communism has fueled political conflicts and wars throughout history, such as the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union.
- Global Interdependence:Capitalism has created an interconnected global economy, with countries relying on each other for trade and resources.
Overlapping Features
Despite their fundamental differences, capitalism and communism share certain overlapping features. These similarities arise from the shared human experiences of economic organization and political governance.
Economic Structures
Both capitalism and communism involve the production and distribution of goods and services. In capitalism, this is primarily driven by private ownership of the means of production, while in communism, the means of production are collectively owned.
However, both systems recognize the need for economic efficiency and growth. They both employ markets to allocate resources, although the extent of market intervention varies. In capitalism, markets are largely unregulated, while in communism, they are centrally planned.
Political Ideologies, Capitalism and communism venn diagram
Both capitalism and communism are political ideologies that seek to shape the organization of society. Capitalism emphasizes individual liberty, free markets, and limited government intervention. Communism, on the other hand, promotes social equality, collective decision-making, and a strong central government.
Despite their contrasting ideologies, both systems share a desire for order and stability. They both recognize the need for a system of laws and institutions to govern society and ensure the well-being of its citizens.
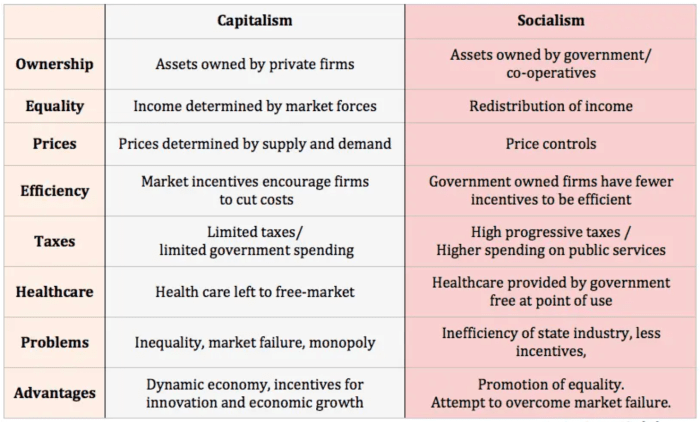
Critical Perspectives: Capitalism And Communism Venn Diagram
Capitalism and communism have been the subject of extensive critique, with both systems facing criticism for their inherent strengths and weaknesses. This section provides a critical analysis of these ideologies, highlighting their potential pitfalls and benefits.
Capitalism has been criticized for its emphasis on individualism and profit maximization, which can lead to income inequality, exploitation of workers, and environmental degradation. Additionally, the profit-driven nature of capitalism can prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability.
Strengths of Capitalism
- Economic efficiency: Capitalism promotes competition and innovation, leading to increased productivity and economic growth.
- Individual freedom: Capitalism emphasizes individual rights and freedoms, including the right to own property and pursue economic opportunities.
- Consumer choice: Capitalism provides consumers with a wide range of goods and services to choose from.
Weaknesses of Capitalism
- Income inequality: Capitalism can lead to significant disparities in wealth and income, creating social divisions.
- Exploitation of workers: In pursuit of profit maximization, some capitalist systems may exploit workers by paying low wages or providing poor working conditions.
- Environmental degradation: The profit-driven nature of capitalism can lead to unsustainable practices that damage the environment.
Communism, on the other hand, has been criticized for its authoritarian nature, suppression of individual rights, and inefficiency in resource allocation. The centralized planning and control inherent in communism can stifle innovation and economic growth.
Strengths of Communism
- Economic equality: Communism aims to eliminate economic inequality by distributing wealth and resources more evenly.
- Social welfare: Communist systems often provide comprehensive social welfare programs, such as healthcare, education, and housing.
- Collective decision-making: Communism emphasizes collective decision-making, which can promote social cohesion and inclusiveness.
Weaknesses of Communism
- Authoritarianism: Communist systems often require a strong central authority to implement and enforce policies, which can lead to suppression of individual rights.
- Inefficiency: Centralized planning can be inefficient, leading to shortages, misallocation of resources, and slow economic growth.
- Lack of innovation: The emphasis on collective decision-making and suppression of individual incentives can stifle innovation and creativity.
General Inquiries
What are the key differences between capitalism and communism?
Capitalism emphasizes private ownership of property and market competition, while communism advocates for collective ownership of property and central planning.
What are the similarities between capitalism and communism?
Both capitalism and communism aim to achieve economic growth and social order, although they differ in their methods.
Which system is more effective in promoting economic development?
The effectiveness of capitalism and communism in promoting economic development is a subject of ongoing debate, with evidence supporting both sides.