NFPA fire hose testing time is a critical aspect of fire safety, ensuring that hoses meet performance standards and are ready to perform when needed. This guide delves into the significance of NFPA testing, its various types, equipment used, and the importance of inspection and maintenance for fire hoses.
Regular testing and maintenance of fire hoses are crucial to guarantee their reliability and effectiveness in emergency situations. This comprehensive overview provides valuable insights into the NFPA fire hose testing time requirements, empowering you with the knowledge to maintain optimal fire safety.
NFPA Fire Hose Testing Standards

NFPA fire hose testing standards play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of fire hoses used by firefighters. These standards establish comprehensive guidelines for testing fire hoses to evaluate their performance and adherence to safety regulations.
NFPA standards cover various aspects of fire hose testing, including:
- Hydrostatic Testing:This test subjects the hose to high water pressure to check its strength and integrity.
- Flow Testing:This test measures the water flow rate through the hose to ensure it meets specified requirements.
- Friction Loss Testing:This test determines the pressure loss due to friction within the hose, which affects the water flow rate.
Each type of test has specific requirements and pass/fail criteria. The following table summarizes the key elements of each test:
| Test | Frequency | Duration | Pass/Fail Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrostatic Testing | Annually | 5 minutes | No leaks, bursts, or ruptures |
| Flow Testing | Annually | 30 seconds | Flow rate meets specified requirements |
| Friction Loss Testing | Every 3 years | Variable | Friction loss does not exceed specified limits |
Test Equipment and Procedures
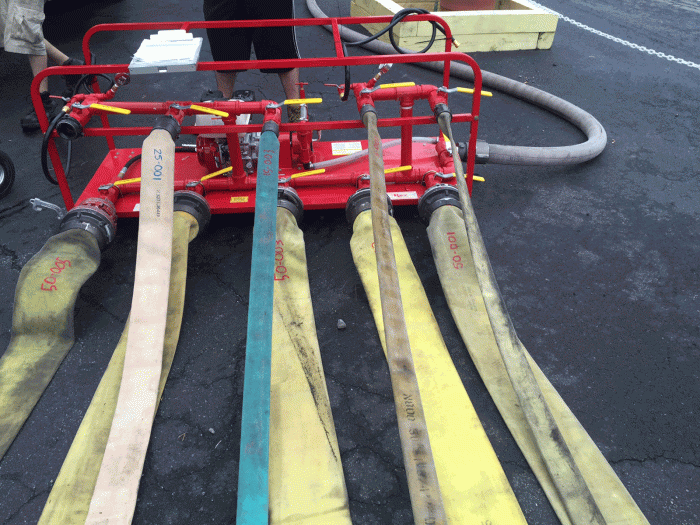
NFPA fire hose testing requires specific equipment and follows established procedures to ensure accurate and reliable results. This equipment and procedures are designed to assess the performance of fire hoses and ensure they meet the required standards.
Equipment
- Flow meters:Measure the volume of water flowing through the hose.
- Pressure gauges:Measure the pressure inside the hose during testing.
- Nozzles:Used to control the flow of water and create different flow patterns.
Procedures
NFPA fire hose testing involves several types of tests, each with its own specific procedures:
- Flow test:Measures the flow rate of water through the hose.
- Pressure test:Assesses the ability of the hose to withstand internal pressure.
- Burst test:Determines the maximum pressure the hose can handle before bursting.
Each test follows a standardized procedure to ensure consistency and accuracy. These procedures involve connecting the equipment to the hose, setting up the test parameters, and recording the results.
The testing process typically involves the following steps:
- Prepare the hose and equipment.
- Connect the equipment to the hose.
- Set up the test parameters.
- Conduct the test.
- Record the results.
- Evaluate the results against the NFPA standards.
Inspection and Maintenance

Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for ensuring optimal fire hose performance and extending its lifespan. These measures help identify potential issues early on, preventing failures and ensuring the hose is ready for use in an emergency.
NFPA fire hose testing time is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of fire hoses. In the spirit of community and brotherhood, the Omega Psi Phi 4th District actively promotes fire safety and emergency preparedness. By adhering to NFPA fire hose testing guidelines, we collectively contribute to the well-being of our communities.
Visual Inspections, Nfpa fire hose testing time
Visual inspections should be conducted regularly, checking for:
- Cuts, abrasions, or tears in the hose cover
- Cracks, bulges, or blisters on the lining
- Loose or damaged couplings and fittings
- Corrosion or rust on metal components
- Mildew or mold growth
Physical Checks
Physical checks involve testing the hose’s functionality and integrity:
Pressure testing
Verifies the hose’s ability to withstand specified pressure without leaking or bursting
Flow testing
Measures the water flow rate through the hose to ensure it meets required standards
Ladder test
Assesses the hose’s ability to support a ladder and firefighters’ weight
Roll-up test
Checks the hose’s flexibility and ability to be rolled up and stored properly
Inspection and Maintenance Schedule
A comprehensive inspection and maintenance schedule should be established to ensure regular checks and timely repairs or replacements. The frequency of inspections and tests may vary depending on the hose’s usage, storage conditions, and manufacturer’s recommendations.A typical inspection and maintenance schedule may include:
- Visual inspections: Monthly
- Pressure testing: Annually
- Flow testing: Every 3-5 years
- Ladder test: Every 5 years
- Roll-up test: As needed
By adhering to a regular inspection and maintenance schedule, fire departments can ensure their fire hoses are in optimal condition, ready to perform effectively when needed.
Failure Analysis and Troubleshooting: Nfpa Fire Hose Testing Time
Fire hose failures during testing can compromise firefighting operations, leading to safety risks and ineffective fire suppression. Understanding the common causes of failures and implementing troubleshooting steps is crucial for maintaining hose integrity and ensuring operational readiness.
Troubleshooting Steps
When a fire hose fails during testing, a systematic troubleshooting approach can help identify and resolve the issue efficiently:
- Inspect the Hose:Visually examine the hose for any visible damage, leaks, or signs of wear.
- Check Connections:Ensure that all couplings and fittings are properly tightened and free from debris.
- Verify Pressure:Confirm that the testing pressure is within the specified range for the hose type.
- Examine Water Flow:Observe the water flow through the hose and check for any restrictions or leaks.
- Test Multiple Sections:If possible, isolate and test different sections of the hose to pinpoint the location of the failure.
Potential Failures and Solutions
Common causes of fire hose failures during testing include:
- Leaks:Caused by damaged or loose fittings, worn gaskets, or punctures in the hose material.
- Burst Hose:Excessive pressure or weakened hose fabric can lead to a hose rupture.
- Coupling Failure:Faulty or improperly installed couplings can detach or fail under pressure.
- Obstructions:Debris, ice, or other foreign objects can block the water flow and cause pressure buildup.
- Abrasion or Wear:Prolonged use, dragging, or improper storage can damage the hose surface.
Corresponding solutions for these failures include:
- Leaks:Replace damaged fittings, tighten connections, or repair punctures.
- Burst Hose:Discard the damaged hose and replace it.
- Coupling Failure:Reinstall the coupling correctly or replace it if damaged.
- Obstructions:Flush the hose to remove debris or replace the obstructed section.
- Abrasion or Wear:Repair minor abrasions or replace the hose if it is severely damaged.
Documentation and Reporting

Accurate documentation and reporting of fire hose testing results are crucial for maintaining hose integrity, ensuring compliance, and facilitating effective decision-making.
NFPA 1962 mandates recordkeeping and the submission of test reports to document the condition and performance of fire hoses. These records serve as a historical record for future reference and provide evidence of hose maintenance and testing.
Recordkeeping Requirements
- Maintain records of all hose tests, including the date, type of test, test results, and any repairs or maintenance performed.
- Store records in a secure and easily accessible location for at least five years.
- Provide test reports to the hose manufacturer, AHJ, or other designated parties upon request.
Sample Report Template
A sample report template should include the following essential information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Hose Identification | Manufacturer, model, serial number, size, length |
| Test Date | Date the test was conducted |
| Test Type | Hydrostatic pressure test, flow test, etc. |
| Test Results | Pressure achieved, flow rate, any observed defects |
| Repairs or Maintenance | Details of any repairs or maintenance performed after the test |
| Tester’s Name and Certification | Name and certification of the qualified tester |
Essential Questionnaire
What is the purpose of NFPA fire hose testing?
NFPA fire hose testing ensures that hoses meet performance standards, ensuring they are reliable and ready to use in emergency situations.
How often should fire hoses be tested?
The frequency of fire hose testing varies depending on the type of hose and its intended use. Refer to the specific NFPA standards for detailed guidelines.
What are the common causes of fire hose failures during testing?
Common causes include leaks, burst hoses, and nozzle malfunctions. Proper inspection and maintenance can help identify and address potential issues before testing.
